Feb 23rd 2026

Article by PolicyBee
The last thing you want to hear when you claim is that your insurance won’t cover your total loss. Or that your insurer is declining (quite within their rights) to pay the full value of your claim.
But either can be the very real and damaging consequences of being underinsured.
Underinsurance rears its troublesome head when your level of cover is less than a claim’s potential total value. The difference between the two means the person or business claiming is out of pocket from the get-go.
So, say you insure your office contents for £40,000 but, after a burglary, it turns out replacing all your kit will cost at least £50,000. You’re down £10,000 already. Ouch.
Then there’s the ‘average rule’ insurers use to calculate claims. It applies to some (but not all) property and business interruption policies. And it means if you’re underinsured, they can reduce the amount they pay you by the same proportion you’re underinsured.
In this case, that’s £40,000 worth of equipment cover minus 20% (£8,000) underinsured, so a total payout of only £32,000….£18,000 shy of the true replacement cost. Double ouch.
Underinsurance can happen when you undervalue the cost of replacing all your kit. Or when you miss something off the list – like carpets, furniture, fixtures, fittings, or hired equipment.
It can also happen when you value your contents at the price you originally paid for them. Remember, your level of cover should be enough to repair or replace all your equipment if it was wiped out today – from your smallest stapler to your most expensive tech. So, sifting through old receipts won’t help.
Better, too, to overestimate how much your stuff’s worth than find yourself short. If your cover includes stock, you might want wiggle room for seasonal stock increases, like the pre-Christmas rush. Same goes for working out the potential replacement value for any new equipment you buy.
Once you’ve worked out the cost of everything – and we mean everything – you can choose the most appropriate level of cover for your business. Then you’ll have the best chance of making sure you’re not left underinsured and having to make up the shortfall if you ever have to claim.
Underinsurance goes beyond equipment. In fact, you can be underinsured for any type of insurance in terms of simply not having enough cover. But here’s where we see it most often:
Underinsurance can leave you seriously on the back foot. So it’s important to regularly review your cover and make sure you have enough – and not always just before your annual renewal. Your circumstances can change considerably in the twelve months between buying insurance and renewing it, and your cover needs to keep pace.
We’d advise going through your insurance portfolio on a regular basis and taking a realistic view on whether you have enough to allow for a worst-case scenario. Take your time working it out – better yet, keep a spreadsheet you can keep on updating.
One last tip. If you’re calculating the rebuild cost of a commercial property you own, it’s best to get a surveyor’s quote or speak to your mortgage lender. The Building Cost Information Service (BCIS) has a handy online calculator.
Any pains you take when working out how much cover you should have are worth it. Because the consequences of underinsurance can be serious in two ways: leaving you unable to claim for your full loss, and making you susceptible to the average rule, reducing your claim further.
That’s a double whammy that can seriously affect your finances.
Read more on how not to be underinsured.
Looking for small business insurance? Click here to get your personalised quote with PolicyBee today and protect your business with confidence.
Feb 13th 2026

If you’re setting up a limited company in the UK, one of the first choices you’ll make is your registered office address. Many directors use their home address because it’s simple, free, and available straight away.
But the simplest option isn’t always the right one. Before you decide, it helps to understand what this address is used for — and what changes once it appears on the public record.
Your registered office address is your company’s official address. Companies House uses it for formal correspondence such as confirmation statement reminders and legal notices. It doesn’t have to be where you work day to day, it just needs to be a real UK address where official mail can be delivered.
It’s also shown on the public Companies House register, which means anyone can look it up online for free.
Yes. UK company law allows you to use your home address as your registered office address, as long as it’s a physical address in the UK (not a PO Box).
For many new directors, it feels like the obvious option: nothing to arrange, no extra cost, and it works fine if you’re starting small and working from home.
However, there are a few drawbacks that often only become clear later on.
Once your home address is your registered office address, it becomes public. It appears on Companies House and is often picked up by third-party sites, data services, and mailing lists.
That can mean:
Even if this doesn’t feel like a concern at the start, many directors find it becomes one as the business grows.
Most businesses won’t run into problems, but sharing a residential address publicly can increase unwanted contact. It can also blur boundaries. Some people assume an address is somewhere they can visit or treat it as a sign you’re always ‘available’.
Over time, that overlap between work and home can become stressful.
Your registered office address can shape first impressions. A residential address may make a company look smaller or less established, especially when you’re dealing with corporate clients, investors, or potential partners. In some sectors, a professional address helps build trust sooner.
A registered office address service lets you use a different UK address for official company purposes while still working from home (or anywhere else).
Typically, this means:
If you don’t need a physical office but you do want a bit more separation and peace of mind, it’s a practical option.
You can, and plenty of directors do. The key is understanding the trade-offs before you register. Privacy, boundaries, and how your company looks on paper are all worth thinking through early.
For many online or service-based businesses, using a registered office service from day one avoids hassle later and keeps things more streamlined.
At MYCO, our address services give your company a professional base. With locations in London, Ipswich, and Edinburgh, you can build credibility from day one.
We handle your official mail and keep everything in one place, so you can focus on running your business.
Feb 4th 2026

At MYCO, we believe in supporting our local communities and giving back. That’s why we’re delighted to announce our Charity of the Year for 2026: St Elizabeth Hospice. This partnership is a chance for all of us to come together, raise funds, and support people and families across our region when they need it most.
St Elizabeth Hospice is an independent Suffolk charity that provides specialist care and support for people living with progressive and life-limiting illnesses, as well as their families and carers. Their focus is always on the individual — helping improve quality of life and ensuring people feel as comfortable as possible, in the place that’s right for them.
They have been providing hospice care for more than 30 years, with patient care beginning in 1989. Since then, their work has made a real difference to thousands of local people each year.
A key part of what they do is offer care in the setting that suits each person best — whether that’s at home, out in the community, or within a hospice. Their teams provide multi-disciplinary support and work closely with other health and community services, helping people access the right care with dignity, compassion, and choice.
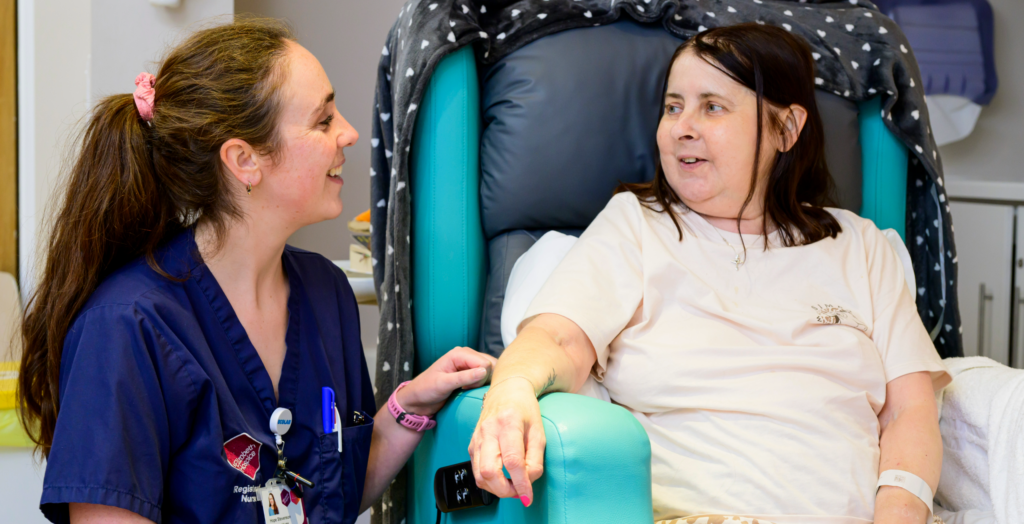
By choosing St Elizabeth Hospice as our Charity of the Year, we can focus our fundraising and awareness efforts on a cause that supports so many people locally. Their services are free to patients, and much of their funding depends on fundraising and community support — which means every donation really does help.
Whether it goes towards specialist care, equipment, or support for families, each contribution plays a part in helping the Hospice continue their vital work.
Over the coming year, we’ll be getting involved in St Elizabeth Hospice fundraising activities and running our own MYCO-led events to support them. If you’d like to help, you can donate directly by clicking here — every contribution, big or small, makes a difference.
